Understanding Osteoporosis and Parathyroid Hormone
Osteoporosis is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by a decrease in bone density, which can lead to an increased risk of fractures. In this article, we will explore the role of parathyroid hormone in osteoporosis treatment and discuss how it can help improve bone health.
In order to understand the role of parathyroid hormone in osteoporosis treatment, it's essential to first understand what this hormone is and how it affects our bones. Parathyroid hormone, or PTH, is a hormone produced by the parathyroid glands, which are located behind the thyroid gland in the neck. This hormone plays a crucial role in regulating calcium levels in the blood, which is essential for maintaining healthy bones.
The Connection between Parathyroid Hormone and Bone Health
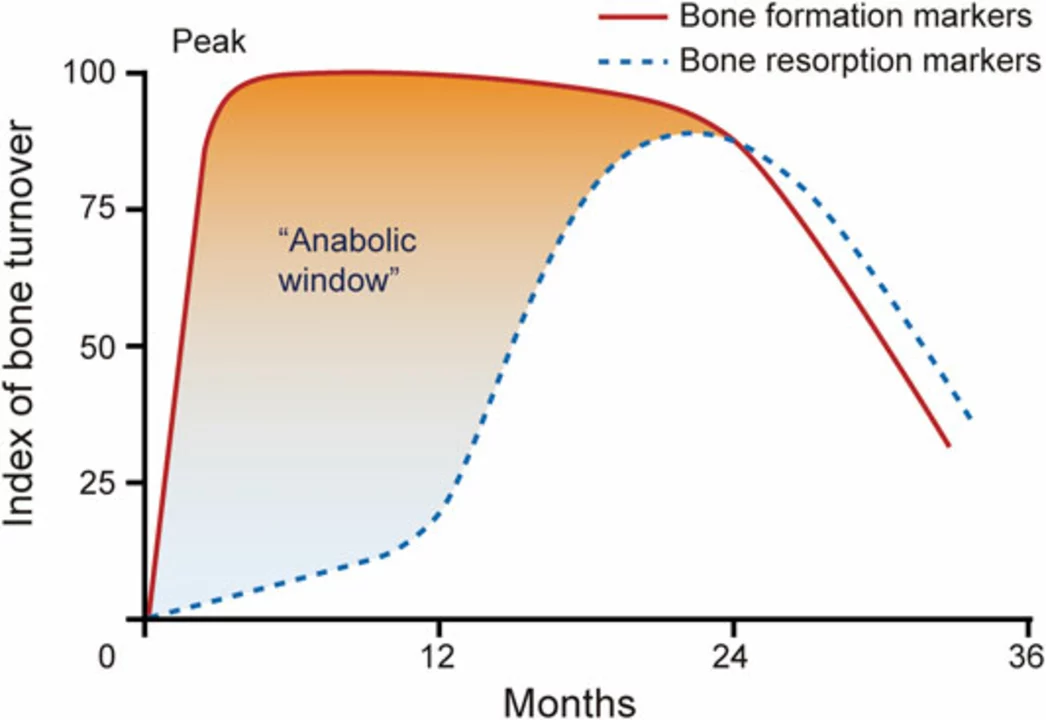
PTH is responsible for maintaining the balance of calcium and phosphorus in our body. When calcium levels in the blood are too low, PTH stimulates the release of calcium from the bones, increasing its concentration in the blood. This process is known as bone resorption. At the same time, PTH also promotes the kidneys to reabsorb calcium, preventing its loss through urine.
While this process is essential for maintaining proper calcium levels in the body, excessive bone resorption can lead to a decrease in bone density and an increased risk of fractures, which is the main characteristic of osteoporosis. Therefore, understanding the role of PTH in bone health is crucial for developing effective treatments for osteoporosis.
Parathyroid Hormone as a Treatment for Osteoporosis
Researchers have discovered that administering synthetic PTH, known as teriparatide, can help stimulate bone formation and increase bone density in people with osteoporosis. Teriparatide is a recombinant form of human parathyroid hormone and is currently approved for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men at high risk of fractures.
Teriparatide works by stimulating the osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation, and increasing the overall bone mass. This, in turn, helps reduce the risk of fractures in people with osteoporosis.
How Teriparatide is Administered
Teriparatide is typically administered as a daily subcutaneous injection in the thigh or abdomen. The recommended dosage is 20 micrograms per day, and the treatment duration should not exceed 24 months, as it may increase the risk of developing osteosarcoma, a rare type of bone cancer.
It is essential for patients to receive proper training on how to administer the injections and to follow the recommended dosing schedule to maximize the benefits of teriparatide treatment.
Benefits of Parathyroid Hormone Treatment
Several clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of teriparatide in increasing bone density and reducing the risk of fractures in people with osteoporosis. Some of the benefits of PTH treatment include:
- Increased bone density: Teriparatide has been shown to significantly increase bone mineral density in the lumbar spine, hip, and other skeletal sites.
- Reduced fracture risk: Studies have reported a significant reduction in the risk of vertebral and non-vertebral fractures in patients treated with teriparatide.
- Improved quality of life: By reducing the risk of fractures, PTH treatment can help improve the overall quality of life for people with osteoporosis, allowing them to maintain their independence and engage in daily activities without the constant fear of fractures.
Side Effects of Teriparatide Treatment
As with any medication, there are potential side effects associated with teriparatide treatment. Some of the most common side effects include:
- Injection site reactions: Redness, pain, or swelling at the injection site are common but usually mild and resolve on their own.
- Nausea and dizziness: Some patients may experience mild to moderate nausea and dizziness, especially during the first few weeks of treatment.
- Leg cramps: Muscle cramps in the legs are a less common side effect but can be managed with proper stretching and hydration.
It is essential to discuss any side effects with your healthcare provider, who can help determine if teriparatide is the right treatment option for you.
Who Should Not Use Teriparatide
Teriparatide is not suitable for everyone. People with certain medical conditions or a history of bone cancer should not use this medication. Some of the contraindications for teriparatide treatment include:
- Paget's disease of bone: This is a condition that affects the normal bone remodeling process, leading to enlarged and weakened bones.
- Hypercalcemia: People with high blood calcium levels should not use teriparatide, as it may worsen their condition.
- Severe renal impairment: Teriparatide is not recommended for people with severe kidney problems, as it may increase the risk of hypercalcemia.
Monitoring and Follow-Up during Teriparatide Treatment
It is essential for patients undergoing teriparatide treatment to have regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider. This allows the provider to monitor the patient's progress, assess the effectiveness of the treatment, and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
During these appointments, the healthcare provider may perform a physical examination, review the patient's medical history, and order laboratory tests to monitor blood calcium levels and other parameters related to bone health. By closely monitoring the patient's progress, the healthcare provider can ensure that the treatment is both safe and effective.
Combining Parathyroid Hormone Treatment with Other Osteoporosis Therapies
In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend combining teriparatide treatment with other osteoporosis therapies, such as bisphosphonates or denosumab. This combination therapy can help enhance the overall effectiveness of the treatment and further reduce the risk of fractures.
It is crucial for patients to discuss their treatment options with their healthcare provider, who can recommend the most appropriate combination of therapies based on the patient's individual needs and medical history.
Conclusion
In conclusion, parathyroid hormone plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health, and its synthetic form, teriparatide, has shown promising results in the treatment of osteoporosis. By increasing bone density and reducing the risk of fractures, PTH treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for people with osteoporosis. However, it is essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine if teriparatide is the right treatment option for them and to closely monitor their progress throughout the treatment process.

liam martin
May 28, 2023 AT 02:00When I think about parathyroid hormone, I imagine a lone knight charging through the bone‑marrow battlefield, wielding calcium like a gleaming sword. The article paints teriparatide as the hero that finally tips the scales in favor of the frail skeleton. Yet, every hero has a shadow, and the risk of osteosarcoma looms like a distant storm. It’s a dramatic dance between hope and caution, and we, the spectators, are left hanging on every injection. In the end, the real question is whether we trust the knight’s promise or keep our armor untouched.
Ria Ayu
May 28, 2023 AT 02:10Reading this reminded me of how many people feel powerless when their doctor mentions “bone density” for the first time. It’s comforting to see the science broken down into everyday language, showing that teriparatide isn’t just a lab trick but a real option for those scared of fractures. I appreciate the gentle reminder to talk with a healthcare provider and to consider personal health history before jumping in. This approach feels like a friendly hand guiding someone through a maze of medical jargon.
maya steele
May 28, 2023 AT 02:20Teriparatide, a recombinant form of human parathyroid hormone, has been extensively studied in phase‑III clinical trials involving over 4,000 patients with severe osteoporosis. The primary mechanism of action involves intermittent stimulation of osteoblast activity, which leads to net bone formation rather than resorption. In the pivotal VERO and ACTIVE studies, patients receiving 20 µg daily demonstrated an average increase of 9 % in lumbar spine BMD after 18 months compared with placebo. Moreover, the incidence of new vertebral fractures was reduced by approximately 65 % in the treatment group. The FDA approval criteria specifically include postmenopausal women and men at high risk of fracture, a definition that aligns with the WHO’s FRAX thresholds for intervention. Dosing is straightforward: a subcutaneous injection administered once daily in the thigh or abdomen, with patients educated on self‑administration techniques. Treatment duration is capped at 24 months due to preclinical findings linking prolonged exposure to an increased risk of osteosarcoma in rodents. Regular monitoring should therefore include serum calcium and 25‑hydroxyvitamin D levels, as well as periodic assessment of renal function. Patients with baseline hypercalcemia or severe renal impairment are contraindicated, as the hormone can exacerbate calcium overload. Injection‑site reactions, such as erythema and mild pain, are generally self‑limited and do not necessitate discontinuation. Nausea and transient dizziness have been reported, particularly during the initial weeks of therapy, and can often be mitigated by taking the dose with a light snack. Orthopedic follow‑up should incorporate dual‑energy X‑ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans at six‑month intervals to quantify BMD response. For individuals who have completed the full course, transitioning to antiresorptive agents such as bisphosphonates or denosumab can help consolidate gains in bone mass. Economic considerations also play a role; while teriparatide is costlier than traditional agents, the reduction in fracture‑related morbidity may offset the upfront expense. Lastly, patient adherence remains a critical determinant of success, underscoring the importance of shared decision‑making and clear communication throughout the treatment journey.
Sharon Lax
May 28, 2023 AT 02:30The pharmacodynamic profile of teriparatide, while ostensibly impressive, suffers from a paucity of real‑world efficacy data beyond controlled trial environments. Its osteoanabolic potential is often overstated, with clinicians neglecting the nuance of receptor desensitization after prolonged exposure. Moreover, the adverse event tableau-ranging from transient hypercalcemia to injection‑site erythema-suggests a suboptimal therapeutic index. In practice, the drug’s cost‑benefit ratio fails to justify its routine incorporation into standard osteoporosis algorithms, especially when cheaper bisphosphonates are available. Ultimately, the literature appears to cherry‑pick favorable endpoints while sidestepping the messy reality of longitudinal compliance.
paulette pyla
May 28, 2023 AT 02:40Ah, the good old American optimism that a synthetic hormone can “fix” our aging skeletons-how quaint. Meanwhile, half the world has been using calcium‑rich diets and sunlight for centuries without needing a daily injection. It’s almost comical that we spend billions on a drug that only works if you trust the pharma lobby more than your grandparents’ folk remedies. But sure, let’s celebrate the miracle of teriparatide while ignoring the fact that it’s practically unavailable in many developing nations, because apparently health equity is a foreign concept.
Benjamin Cook
May 28, 2023 AT 02:50Wow!!! This is game‑changing stuff!!!
karthik rao
May 28, 2023 AT 03:00While the enthusiasm surrounding teriparatide is palpable, the aggregate data still reveal a modest absolute risk reduction in non‑vertebral fractures, which may not justify widespread adoption 🙄. A rigorous cost‑effectiveness analysis frequently places the drug beyond the threshold for public health reimbursement, suggesting that enthusiasm must be tempered by fiscal prudence.
Breanne McNitt
May 28, 2023 AT 03:10I think it’s great that we have such a detailed breakdown of PTH therapy, and it opens the door for us to share personal experiences-like how some of us schedule injection times around workouts or meal plans. Let’s keep this thread alive by swapping tips on managing side effects and staying motivated throughout the 24‑month regimen. The more we collaborate, the better we’ll all navigate the challenges.
Ashika Amirta varsha Balasubramanian
May 28, 2023 AT 03:20From an Indian perspective, it’s worth noting that many patients already consume calcium‑rich foods such as dairy, leafy greens, and millet, which can synergize with teriparatide’s bone‑building effects. However, vitamin D deficiency is prevalent, so ensuring adequate sun exposure or supplementation is essential before initiating therapy. Balancing traditional dietary practices with modern pharmacotherapy can create a holistic approach that respects cultural heritage while embracing scientific advances.
Jacqueline von Zwehl
May 28, 2023 AT 03:30When discussing teriparatide, it’s important to use language that acknowledges diverse experiences and avoids alienating anyone who may feel uncertain about injections. We should remind readers that side‑effects vary and that open communication with healthcare providers can tailor treatment to individual needs. Inclusivity means offering resources in multiple formats-videos, brochures, and community workshops-so everyone can make an informed decision.
Christopher Ellis
May 28, 2023 AT 03:40In the end the hormone is but a reminder that bone, like life, is in constant flux and our attempts to command it reveal both our hubris and our hope