Progesterone: What it does and how to use it safely
Progesterone is a hormone your body makes naturally. People use extra progesterone medically for things like supporting early pregnancy, balancing hormones in menopause, or as part of fertility treatments. It isn’t one-size-fits-all: doses, forms, and goals change a lot depending on why you need it.
How progesterone works and common uses
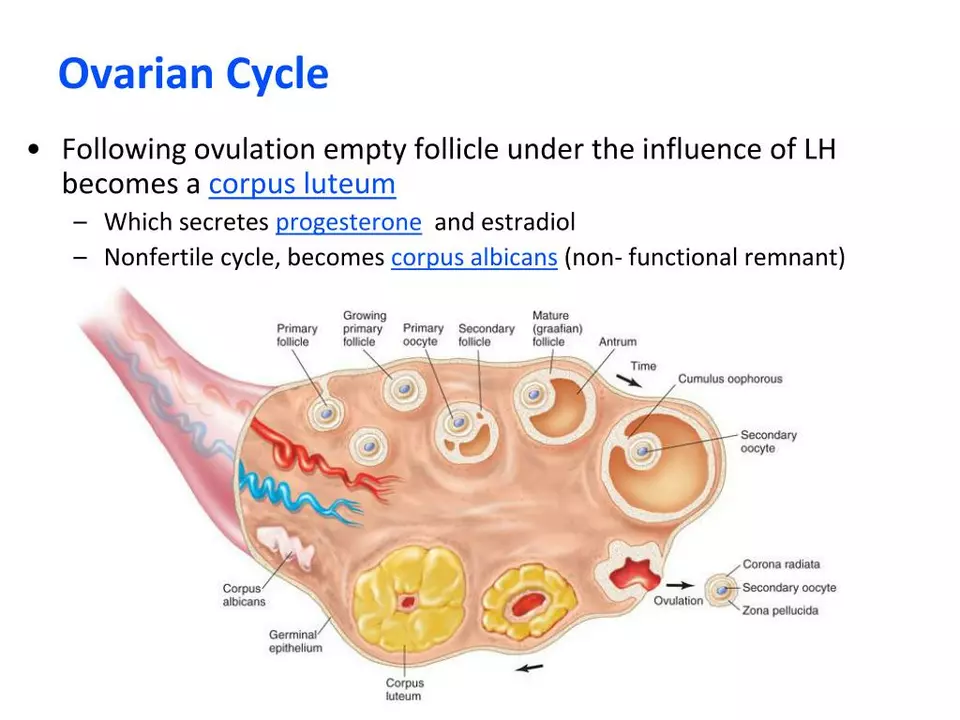
Progesterone prepares the uterus lining for implantation and helps keep a pregnancy in its early stages. In menopause, doctors often combine it with estrogen to protect the lining of the uterus when estrogen alone is prescribed. Fertility clinics use progesterone for luteal phase support after ovulation or embryo transfer. Other uses include treating menstrual irregularities, certain types of abnormal bleeding, and—less commonly—some hormone-driven conditions.
Forms matter. You’ll see progesterone as pills (micronized oral), vaginal gels or suppositories, injections, and sometimes creams or capsules. Vaginal forms deliver hormone directly to the uterus area and are often used in fertility care. Oral forms go through the liver first, which can change effects and side effects. Injections give higher, quicker levels but can be less convenient.
Side effects, safety, and what to watch for
Common side effects are mood swings, bloating, breast tenderness, and sleepiness. Some people notice spotting or changes in their period. Serious reactions are rare but possible—if you have severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, or signs of a blood clot, get medical help right away. If you have a history of breast cancer, blood clots, liver disease, or unexplained vaginal bleeding, talk to your doctor before using progesterone.
Interactions matter. Tell your clinician about all medicines, supplements, and herbs you take—some can change how hormones work. Your doctor may recommend blood tests or follow-up visits depending on the reason you’re taking progesterone. For fertility or pregnancy care, clinics usually give specific timing and dose instructions—follow them closely.
If you’re thinking about buying progesterone online, be cautious. Use licensed pharmacies and read product reviews. Some sites offer helpful guides on safe online buying and brand differences—look for those that explain shipping, storage, and lab testing. Never self-prescribe high doses or change a doctor’s plan without consulting your provider.
Questions to ask your clinician: Why this form of progesterone? How long will I need it? What side effects should I expect and when should I call? Who will monitor my treatment? Clear answers will make the treatment safer and less stressful.
Want more practical reads? Our site has guides on buying specific products, fertility support, and hormone alternatives—check the related articles for step-by-step tips and up-to-date safety advice.